Life Extension Biotin 600 mcg 100 Capsules
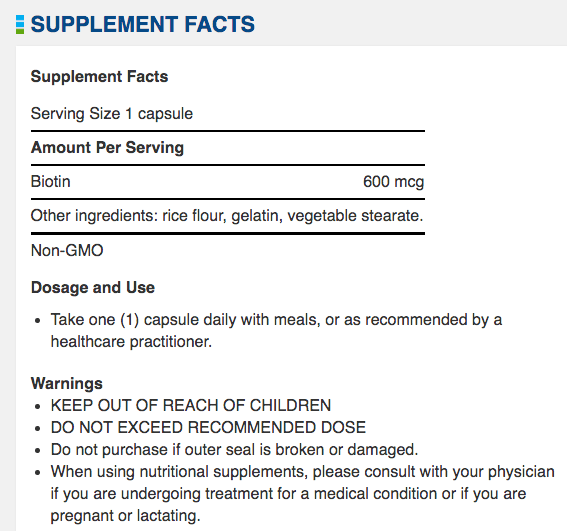
Biotin is an unnumbered member of the water soluble B-complex family, normally only required in minute amounts. Biotin is used as a cofactor of enzymes involved in fatty acid metabolism, gluconeogenesis, and amino acid catabolism, and is essential in maintaining metabolic homeostasis.
Biotin plays an important role in metabolic functioning as a coenzyme carrier of activated carbon dioxide in the TCA cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle). In its coenzyme form, biotin synthesizes glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, and synthesizes and breaks down certain fatty acids and amino acids.
Biotin is an unnumbered member of the water soluble B-complex family, normally only required in minute amounts. Biotin is used as a cofactor of enzymes involved in fatty acid metabolism, gluconeogenesis, and amino acid catabolism, and is essential in maintaining metabolic homeostasis.
More Info on Life Extension Biotin 600 mcg 100 Capsules
† Statements on this website have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease, but rather are dietary supplements intended solely for nutritional use.